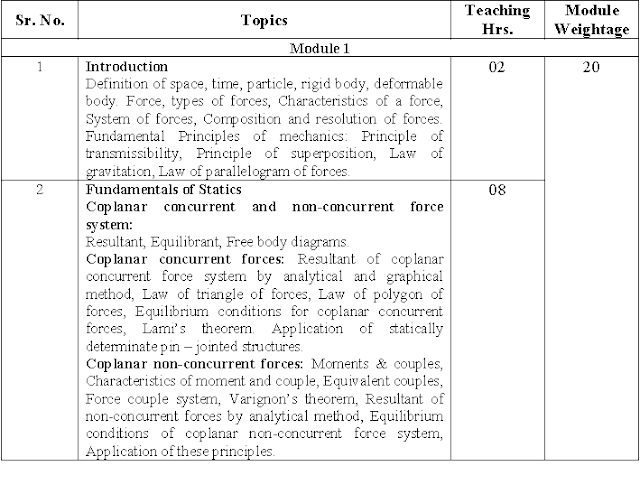
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 1:-
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 2:-
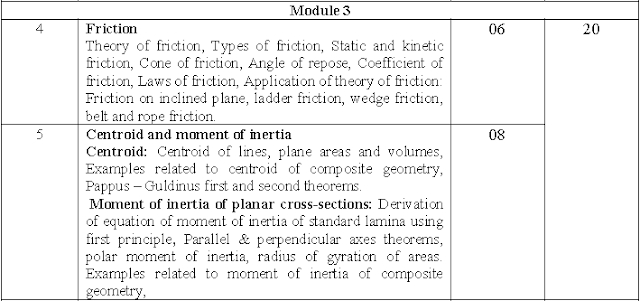
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 3:-
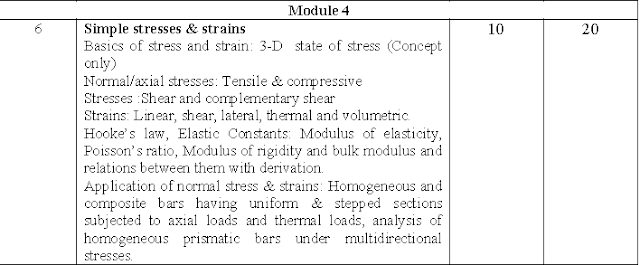
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 4:-
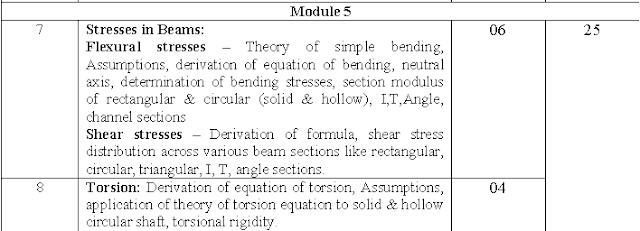
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 5:-
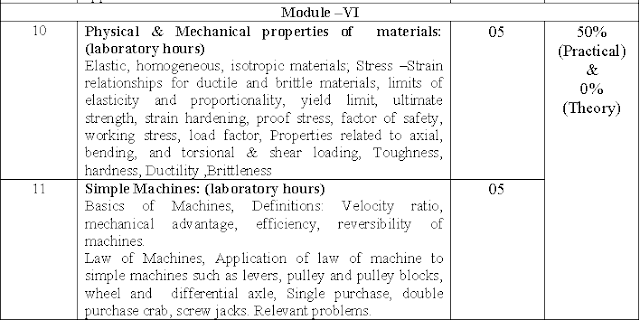
GTU MOS Syllabus Module 6:-
List of Experiments:
The students will have to solve atleast five examples and related theory from each topic as an assignment/tutorial. Students will have to perform following experiments in laboratory and prepare the laboratory manual.
Mechanics of rigid body
1. Equilibrium of coplanar concurrent forces
2. Equilibrium of coplanar non-concurrent forces
3. Equilibrium of coplanar parallel forces: Determination of reactions of simply supported beam
4. Verification of principle of moment: Bell crank lever
5. Determination of member force in a triangular truss
6. Determination of coefficient of static friction using inclined plane
7. Determination of parameters of machines (Any two)
(a) Wheel and differential axles
(b) Single purchase crab
(c) Double purchase crab
(d) System of pulleys
Mechanics of deformable body
8. Determination of hardness of metals: Brinell /Vicker/Rockwell hardness test
9. Determination of impact of metals: Izod/Charpy impact test
10. Determination of compression test on
(a) Metals – mild steel and cast iron
(b) Timber – along and parallel to the grains
11. Determination of tensile strength of metals
12. Determination of shear strength of metals
Design based Problems (DP): (any two)
1. For a real industrial building having roof truss arrangement, (a) take photograph & identify
type of truss, (b) draw sketch of truss with all geometrical dimension, cross sections details,
type of joints, type of support conditions (c) prepare a model of truss (d) identify & determine
types of load acts on it (d) determine support reactions & member forces due to dead load &
live load only.
2. Take a case of the Mery-Go-Round used in the fun park. Draw its sketch showing radius of
wheel, no of seats, capacity of each seats and other related information. Determine the amount
of resultant produced at the centre of wheel during rest position, when (i) it is fully loaded (2)
it is 30% loaded with symmetric arrangement. Draw support arrangement and determine
support reactions. Also determine amount of torque required to start its operation.
3. Prepare working models for various types of beams with different shape of cross section,
supporting conditions and study the effect of cross section on the deflection of beams.
4. Prepare working model of simple lifting machine using different types of pulley systems and
calculate various parameters like load factor, velocity ratio, law of machine, efficiency of
machine etc.





0 comments:
Post a Comment